Bromhexine vs. Other Mucolytics Comparison Tool
Recommended Mucolytic Agent:
Detailed Comparison:
Drug Comparison Overview
Targets disulfide bonds in mucus proteins. Effective for thick sputum in chronic bronchitis. Generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects.
Aggressive mucus breakdown with antioxidant properties. Strong odor may be a drawback. Good for acute infections with oxidative stress.
Stimulates surfactant production in addition to mucus thinning. Useful for bronchodilation. May cause taste disturbance.
Prevents mucus polymerization. Commonly prescribed for chronic bronchitis. May cause GI discomfort.
Over-the-counter expectorant. Increases water content of secretions. Safe for children and pregnant women but less potent.
Key Takeaways
- Bromhexine works by breaking down mucus polymers, making it easier to cough up.
- Acetylcysteine and ambroxol are the closest rivals, each with a distinct mechanism.
- Side‑effect profiles differ - bromhexine is generally well tolerated, while acetylcysteine can cause a strong odor.
- Over‑the‑counter options like guaifenesin are milder but safer for children.
- Choosing the right agent depends on your condition, age, and any existing medications.
When mucus becomes thick and sticky, clearing the airways can feel like an endless battle. Bromhexine is a synthetic mucolytic agent sold as bromhexine hydrochloride that has been used for decades to dissolve bronchial secretions. Bromhexine is popular in many countries, but it isn’t the only game in town. This guide breaks down how bromhexine stacks up against the most common alternatives, so you can pick the one that fits your needs.
What Is Bromhexine and How Does It Work?
Bromhexine belongs to the class of mucolytic agents. Its primary action is to destabilize the disulfide bonds that hold mucus glycoproteins together. By doing so, it reduces the viscosity of the secretions and promotes a more productive cough. The drug is usually taken orally, with a typical adult dose of 8mg three times a day. It reaches peak plasma levels within 30‑60minutes, offering relatively quick relief.
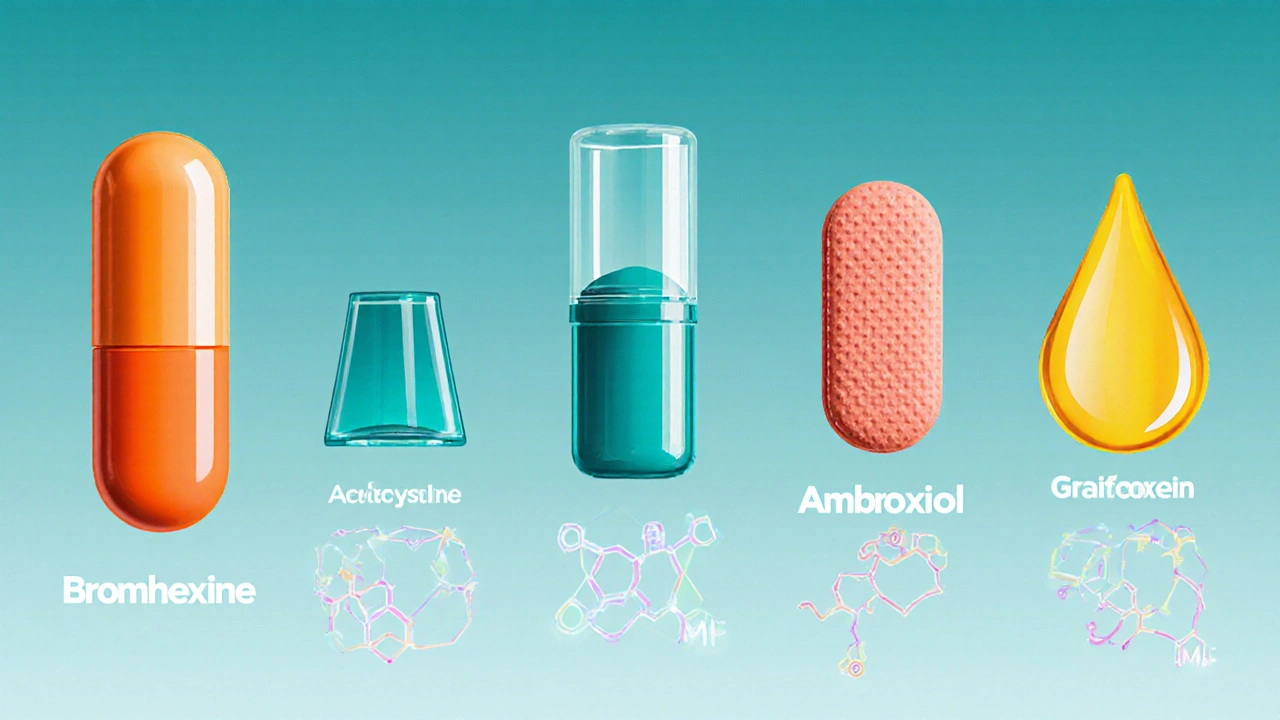

Major Alternatives on the Market
Several other compounds claim to thin mucus or soothe coughs. Below are the most widely used options, each introduced with its own microdata definition.
Acetylcysteine (also known as N‑acetylcysteine) is a classic mucolytic that works by cleaving the same disulfide bonds that bromhexine targets, but it does so more aggressively. It’s available in both oral and inhalation forms, with a standard dose of 600mg daily for adults.
Ambroxol is a metabolite of bromhexine. It shares a similar mechanism but also stimulates surfactant production, which can improve lung compliance. Typical dosing is 30mg three times a day.
Carbocisteine is a mucolytic that reduces mucus viscosity by interfering with its polymerisation. It’s often prescribed for chronic bronchitis, with a dose of 500mg three times daily.
Guaifenesin is an over‑the‑counter expectorant rather than a true mucolytic. It works by increasing the water content of secretions, making them easier to clear. The usual adult dose is 200‑400mg every 4hours, not exceeding 2.4g per day.
Other related concepts worth noting are cough itself, which can be productive (wet) or non‑productive (dry), and respiratory tract infection, the common trigger that leads people to seek mucolytic therapy.
Side‑Effect Profiles Compared
Understanding safety is as important as efficacy. Below is a quick rundown of the most frequent adverse events for each agent.
- Bromhexine: mild gastrointestinal upset, occasional skin rash.
- Acetylcysteine: strong sulfuric odor, nausea, rare bronchospasm when inhaled.
- Ambroxol: taste disturbance, rare allergic reactions.
- Carbocisteine: gastrointestinal discomfort, dizziness in sensitive individuals.
- Guaifenesin: generally well tolerated; high doses may cause hiccups.
Direct Comparison Table
| Agent | Mechanism | Typical Adult Dose | Onset of Action | Key Side Effects | OTC Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bromhexine | Disrupts disulfide bonds in mucus proteins | 8mg three times daily | 30‑60min | GI upset, rash | Prescription in many regions |
| Acetylcysteine | Reduces disulfide cross‑linking; antioxidant | 600mg once daily (oral) or inhalation | 45‑90min | Odor, nausea, bronchospasm | Prescription (some OTC inhalers) |
| Ambroxol | Similar to bromhexine + stimulates surfactant | 30mg three times daily | 30‑45min | Taste change, allergy | Prescription in many countries |
| Carbocisteine | Inhibits mucus polymerisation | 500mg three times daily | 1‑2h | GI discomfort, dizziness | Prescription |
| Guaifenesin | Increases water content of secretions | 200‑400mg every 4h (max 2.4g/day) | 30‑60min | Hiccups, mild GI upset | OTC worldwide |

When to Choose Bromhexine Over the Rest
If you need a drug that specifically targets the structural integrity of mucus while keeping the side‑effect burden low, bromhexine is a solid choice. It’s especially useful for chronic bronchitis patients who experience frequent, thick sputum but cannot tolerate the strong odor of acetylcysteine.
However, if you are dealing with an acute viral infection and want an antioxidant boost, acetylcysteine may be preferable. For patients who also need a mild bronchodilatory effect, ambroxol’s surfactant‑stimulating property can be advantageous.
Children and pregnant women often default to guaifenesin because of its safety record, even though it’s less potent than the prescription options.
Practical Tips for Using Bromhexine Safely
- Take the medication after meals to reduce stomach irritation.
- Do not combine with other strong mucolytics unless a physician advises.
- Stay hydrated - water helps the drug work more efficiently.
- If you notice a rash or persistent nausea, stop the drug and consult a healthcare professional.
- Check for drug interactions: bromhexine can increase the absorption of some antibiotics, potentially raising their effect.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use bromhexine for a common cold?
Yes, bromhexine can help relieve the thick mucus that often accompanies a cold, but it won’t treat the viral cause. Use it alongside rest, fluids, and any recommended symptom relievers.
How quickly does bromhexine start working?
Most adults feel a reduction in mucus thickness within 30 to 60 minutes after the first dose.
Is bromhexine safe for children?
Safety data for children under 12 are limited. Pediatric doctors usually prefer guaifenesin or lower‑dose ambroxol for kids.
Can I take bromhexine with antibiotics?
Yes, bromhexine often improves antibiotic penetration by clearing mucus, but always follow your doctor’s guidance to avoid dosing conflicts.
What should I do if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for the next scheduled dose. In that case, skip the missed one and continue your regular schedule. Do not double‑dose.
Choosing the right mucolytic boils down to your specific health situation, how quickly you need relief, and how your body reacts to each compound. By comparing bromhexine with its main rivals, you now have a clearer roadmap to smoother breathing.



Emily Moody
Patriotic physicians know that Bromhexine’s pharmacodynamics are the unsung hero of mucus dissolution, wielding disulfide‑bond disruption with the ferocity of a battlefield artillery barrage. Its bioavailability outstrips many over‑the‑counter rivals, delivering a swift, decisive strike against tenacious sputum that would otherwise choke the spirit of our great nation. While acetylcysteine fights with a pungent odor reminiscent of industrial exhaust, Bromhexine glides in like a sleek fighter jet, silent yet lethal. No wonder clinicians hoist it as a banner of therapeutic liberty, championing clear airways for the hardworking citizenry. If you demand a mucolytic that doesn’t cower before a stubborn cough, this is the vehicle of choice-engineered for victory, calibrated for safety.
Prateek Kohli
Great rundown! 👍 The comparison makes it easy to see when Bromhexine shines versus the others, especially for chronic bronchitis where steady mucus thinning matters. The table’s layout is spot‑on, and the practical tips on hydration are a nice touch. Keep the balanced info coming 😊
Patrick Price
i think ths article is verry helpful but i have a qestion about the dosage for older peopel could u clarifiy if 8mg three times a day is safe for them? also is there any risk of intercting with common antihistamine i take daily
Travis Evans
Yo folks, love the practical vibe here. If you’re juggling a cold and need to stay on the move, Bromhexine’s quick onset can be a game‑changer. Just remember to sip plenty of water – it’s the secret sauce that helps any mucolytic work its magic. You’ve got this!
Jessica Hakizimana
It’s uplifting to see a guide that blends science with genuine care. The way the author highlights both efficacy and safety reminds us that medicine is as much an art as a science. By weighing each option, we empower ourselves to make choices that honor our bodies and our daily lives. Keep the positive energy flowing, and thank you for shedding light on these often‑overlooked details.
peter derks
Exactly, Travis! Adding a dash of humor never hurts either – “water is the secret sauce” had me smiling while I’m sipping tea. Hydration really does amplify the drug’s mucolytic power, and it’s a simple habit we can all stick to.
Sarah DeMaranville
Honestly the guide overstates bromhexine’s benefits it’s just another prescription drug with a modest effect
Edward Leger
When considering mucolytic therapy, it is essential to adopt a measured, contemplative stance that acknowledges both physiological mechanisms and patient experience. Bromhexine operates by cleaving disulfide bonds within mucus glycoproteins, thereby reducing viscosity and facilitating expectoration. This biochemical action distinguishes it from agents such as guaifenesin, which merely increase water content without altering polymer structure. The onset of action, typically thirty to sixty minutes, aligns well with the needs of individuals seeking prompt relief. Moreover, its side‑effect profile is modest, with gastrointestinal discomfort and occasional rash being the most commonly reported adverse events. In contrast, acetylcysteine, while potent, presents a notoriously strong sulfuric odor that many patients find intolerable. Ambroxol adds a bronchodilatory component through surfactant stimulation, offering a dual benefit in certain obstructive diseases. Carbocisteine, on the other hand, targets mucus polymerisation, which can be advantageous in chronic bronchitis but may cause dizziness in sensitive individuals. The therapeutic landscape thus demands a nuanced appreciation of each agent’s strengths and limitations. Clinical guidelines often recommend tailoring the choice to the specific clinical context, such as acute viral infections versus chronic inflammatory states. Patient adherence is also shaped by factors like dosing frequency, with bromhexine’s thrice‑daily schedule being relatively convenient. Cost considerations cannot be ignored; prescription status may limit accessibility for some populations. Safety during pregnancy remains a critical concern, and the prevailing consensus favors guaifenesin for its established safety record. Ultimately, the decision rests upon a balance of efficacy, tolerability, convenience, and individual patient values. By reflecting on these dimensions, clinicians and patients alike can navigate the mucolytic options with greater clarity and confidence.
Keyla Garcia
Wow, bromhexine totally dominates the mucolytic game! 😱
Ismaeel Ishaaq
Sarah, you’re missing the bigger picture – bromhexine’s modest side effects are a small price for the dramatic improvement in sputum clearance, especially when you compare it to the barely‑effective guaifenesin. Its targeted action on disulfide bonds makes a real difference, and dismissing it as “just another prescription drug” undervalues the science behind it.
Jesse Goodman
Clear and thorough, thanks for the deep dive. 👍
Antara Kumar
While the guide praises bromhexine, we must remember that many countries rely on home‑grown remedies that respect local health traditions. Imported pharmaceuticals should never eclipse indigenous knowledge, especially when they are marketed primarily for profit.
John Barton
Oh sure, because the best way to fight a stubborn cough is to revert to medieval herbal teas while ignoring decades of clinical research. Nothing says “effective treatment” like wine‑stained folklore.
Achint Patel
Jesse, your succinct nod is appreciated; it mirrors the elegance of a well‑crafted sentence-brief yet resonant, much like an optimal mucolytic regimen that does its job without unnecessary fanfare.