Understanding Diabetes and the Importance of Exercise
As someone who has been affected by diabetes, I know how important it is to maintain a healthy lifestyle and engage in regular physical activity. In this article, we will discuss the role of exercise in controlling and preventing diabetes. We will cover various topics, such as understanding the types of diabetes, how exercise can help manage blood sugar levels, and tips for incorporating exercise into your daily routine.
The Two Types of Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2
Before diving into the benefits of exercise, it's crucial to understand the two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in little or no insulin production, causing high blood sugar levels. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body doesn't use insulin properly, leading to insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. While exercise can be beneficial for both types of diabetes, it's particularly helpful for those with Type 2 diabetes since it can help improve insulin sensitivity.
How Exercise Helps Manage Blood Sugar Levels
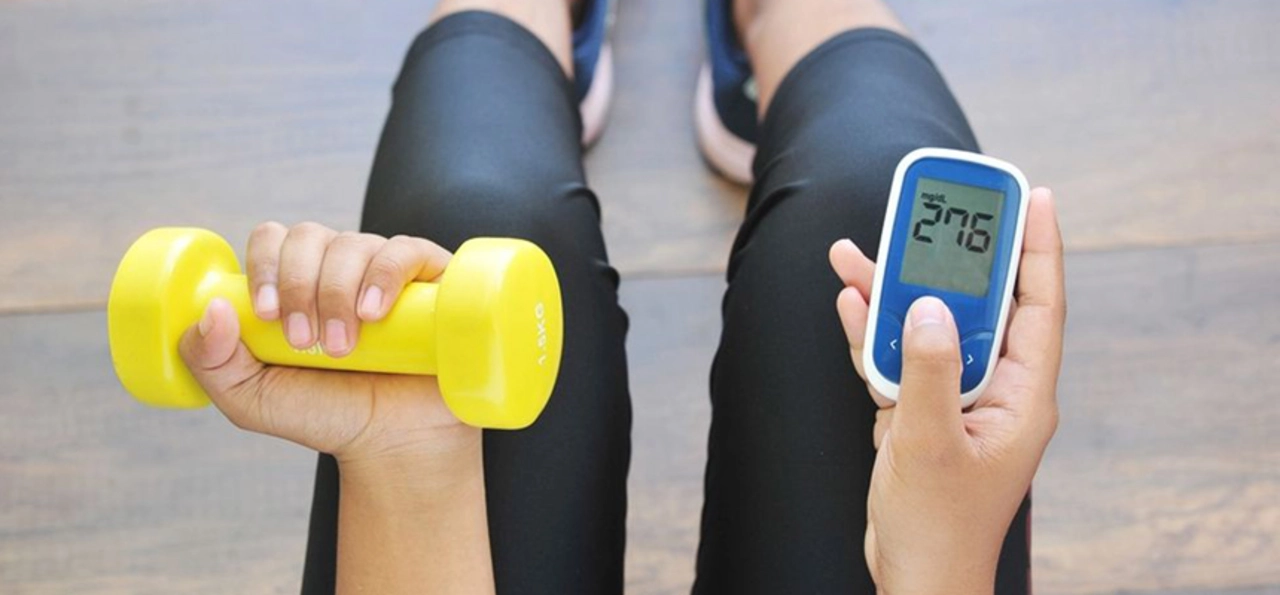
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and controlling diabetes. When we exercise, our muscles use glucose for energy, which helps lower blood sugar levels. Additionally, exercise can increase insulin sensitivity, allowing our cells to better use the available insulin. This means that our bodies need less insulin to transport glucose into our cells.
Moreover, regular exercise can help reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, stroke, and nerve damage. By maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in physical activity, we can significantly reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and improve our overall health.
Choosing the Right Type of Exercise
When it comes to incorporating exercise into your routine, it's essential to choose activities that you enjoy and are suitable for your fitness level. There are three main types of exercise that can help manage diabetes: aerobic exercise, resistance training, and flexibility exercises.
Aerobic exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, helps improve cardiovascular health and can lower blood sugar levels. Resistance training, such as weightlifting or using resistance bands, can help build muscle mass and improve insulin sensitivity. Finally, flexibility exercises, such as yoga or Pilates, can help maintain joint health and prevent injury. It's essential to combine these different types of exercise to achieve the best results in managing diabetes.
Creating an Exercise Plan for Diabetes Management
When creating an exercise plan to manage diabetes, it's crucial to consider your individual needs and preferences. Start by setting realistic goals and gradually increasing the intensity and duration of your workouts. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with two to three sessions of resistance training.
It's also essential to monitor your blood sugar levels before and after exercise, as physical activity can cause fluctuations in glucose levels. Keep a log of your exercise routine and blood sugar levels to track your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your plan. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have any existing health conditions.
Overcoming Barriers to Exercise for People with Diabetes
For many people with diabetes, incorporating regular exercise into their daily routine can be challenging. Common barriers include lack of time, fear of injury, or feeling overwhelmed by the idea of starting a new fitness regimen. However, it's essential to recognize that these obstacles can be overcome with the right mindset and support.
Start by identifying your barriers and brainstorming solutions to overcome them. For example, if time is an issue, consider incorporating short bursts of physical activity throughout your day, such as taking a walk during your lunch break or doing a quick workout at home. If you're worried about injury, work with a personal trainer or healthcare provider to develop a safe and effective exercise plan tailored to your needs. Remember, it's never too late to start exercising and reaping the benefits for your diabetes management.
Staying Motivated and Consistent with Your Exercise Routine
Maintaining motivation and consistency with your exercise routine is crucial for achieving long-term success in managing diabetes. One way to stay motivated is by setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. For example, instead of saying, "I want to exercise more," set a goal like, "I will walk for 30 minutes, five days a week, for the next four weeks."
Another strategy is to find an exercise buddy or join a group fitness class, as social support can significantly impact your motivation and accountability. Finally, remember to celebrate your achievements and reward yourself for meeting your goals. By staying consistent with your exercise routine and focusing on the positive improvements in your health, you can successfully manage and prevent diabetes through regular physical activity.



Tracy Blake
Exercise is like the universe’s way of whispering to your cells: 'Hey, you got this.' 🌱✨ I used to think diabetes was a life sentence, but then I started walking after dinner-just 20 minutes-and suddenly my numbers weren’t screaming anymore. It’s not about becoming an athlete, it’s about becoming a student of your own body. Every step is a conversation with your pancreas, and it’s learning to listen again. I cry sometimes when I see my glucose chart improve-like, actual tears. Not because I’m weak, but because I finally feel like I’m not just surviving. I’m *co-creating* my health. And yeah, I know it sounds hippie-dippie, but science backs it up. Insulin sensitivity isn’t magic-it’s movement. Movement is prayer with your legs.
Leo Lee
You people act like exercise is some kind of miracle cure. It’s not. It’s hard work. And if you’re too lazy to get off the couch, don’t blame your genes or your doctor. I’ve seen Type 2 diabetics who lifted weights three times a week and dropped 80 pounds. No supplements. No magic pills. Just sweat. Stop romanticizing it. Just move. Now. Your future self will thank you-or curse you. Choose wisely.
Isabel Piaggi
im not saying exercise is the answer but like… maybe its part of the answer?? like if you move your body you tell your cells hey we’re still here dont give up on us 😅 i used to think i had to run marathons to be healthy but now i just do yoga in my pajamas and its life changing i mean like… my sugar levels arent perfect but theyre better and i sleep better and i dont feel like a zombie anymore. also pls drink water. i forgot to drink water for a week once and my glucose spiked like a rocket 🚀
Tom McInnes
Well-structured article. The emphasis on combining aerobic, resistance, and flexibility training is evidence-based and practical. I’d add that consistency trumps intensity-especially for older adults or those with comorbidities. A daily 10-minute walk is superior to a weekly 90-minute session followed by three days of inactivity. Also, always check with a physician before initiating resistance training if neuropathy or retinopathy is present.
Stephanie Cepero
I just want to say how much this resonated with me… I was diagnosed two years ago, and I felt so alone. I thought I had to give up everything I loved. But then I started dancing with my daughter in the kitchen-just silly, loud, barefoot dancing-and I realized I didn’t have to “fix” myself to be worthy of health. I’ve lost 30 pounds, my A1C dropped from 8.1 to 6.2, and I actually laugh more now. Thank you for writing this. I’m not just managing diabetes-I’m reclaiming joy. And if you’re out there feeling scared? You’re not alone. We’re here. 💛
Michael Tribone
Love this. Seriously. If you’re reading this and thinking ‘I can’t start today,’ here’s your permission slip: YOU CAN. Even if it’s just standing up and stretching for 2 minutes. Even if it’s walking to the mailbox. That’s a win. I’ve coached dozens of people with diabetes, and the ones who stick with it? They don’t wait for motivation-they build habits. Set a timer. Put on your shoes. Do 5 squats. Then celebrate. Repeat tomorrow. Progress isn’t linear, but it’s real. And you’re not just preventing diabetes-you’re building a life worth living. Now go take a step. I believe in you.