Rifampin and Warfarin: What You Need to Know About the Interaction
When you take rifampin and warfarin, a powerful antibiotic and a common blood thinner. Also known as Rifampicin, rifampin is often used for tuberculosis and other bacterial infections, while warfarin helps prevent dangerous blood clots in people with atrial fibrillation, artificial heart valves, or deep vein thrombosis. This combo isn’t just risky—it’s one of the most well-documented and dangerous drug interactions in medicine.
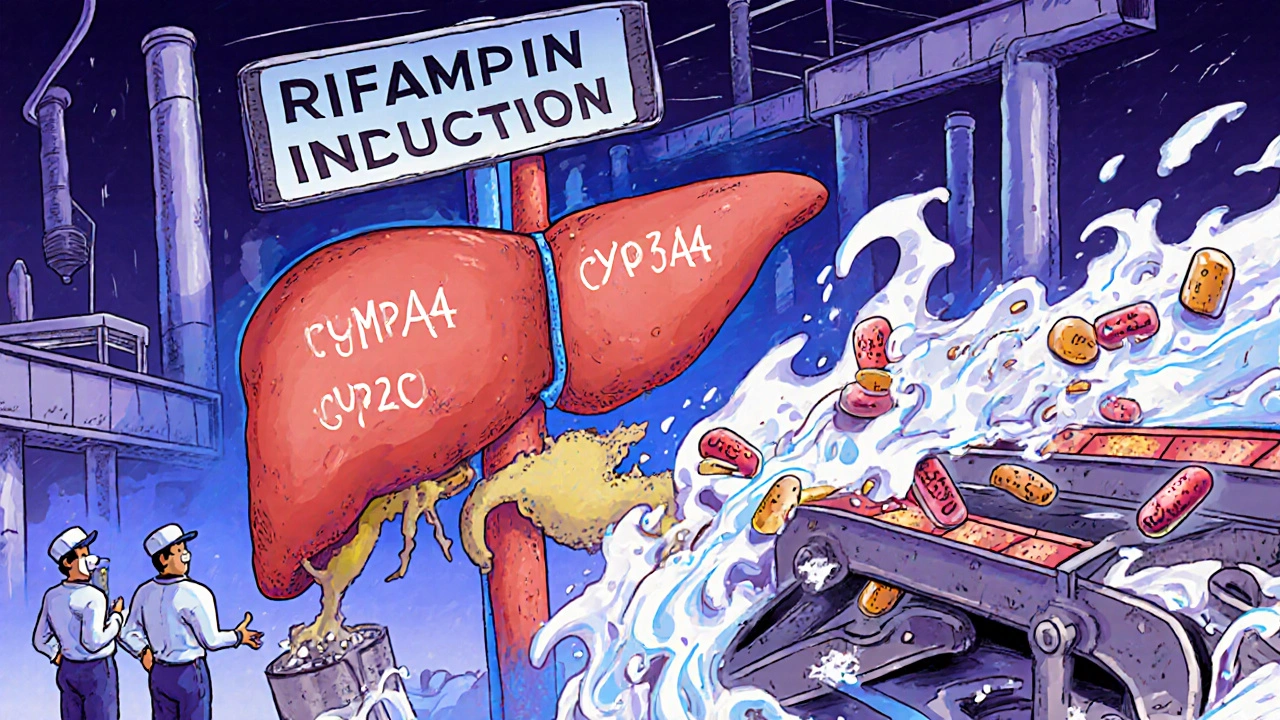
Rifampin speeds up how your liver breaks down warfarin, which means warfarin leaves your body faster than normal. The result? Your blood doesn’t thin as much as it should. That’s not just a lab number—it’s a real risk of stroke, heart attack, or pulmonary embolism. People on warfarin often don’t feel anything changing until it’s too late. That’s why regular INR blood tests are non-negotiable when rifampin is added to your regimen. Studies show INR levels can drop by 50% or more within days of starting rifampin, even if your warfarin dose hasn’t changed.
This isn’t just about the two drugs. It’s about your whole system. Rifampin affects dozens of other medications—birth control pills, antidepressants, seizure meds, even some painkillers. If you’re on warfarin and your doctor prescribes rifampin, ask: What else might this change? Your pharmacist should flag this interaction, but don’t rely on that alone. Keep a list of every pill you take, including supplements and OTC meds. A simple antacid or St. John’s Wort can throw off your INR too. And if you’re switching from rifampin to something else, the effect reverses—your warfarin levels can spike dangerously high, leading to bleeding. That’s why dose adjustments need to be slow and monitored.
There’s no magic fix. You can’t avoid the interaction by changing the time you take the pills. You can’t outsmart it with diet. The only reliable way to manage this is through frequent blood tests and close communication with your care team. If you’re on warfarin and need antibiotics, ask if there’s an alternative to rifampin—like doxycycline or azithromycin—that won’t interfere. If rifampin is your only option, treat your INR checks like appointments you can’t miss.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides and comparisons that help you understand how drug interactions like this play out in practice. From how other antibiotics affect blood thinners to what to do when your meds don’t work as expected, these posts give you the tools to ask smarter questions and stay in control of your health.