Blood Thinners: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your blood has a hard time clotting the right way, blood thinners, medications that reduce the risk of dangerous clots in veins and arteries. Also known as anticoagulants or antiplatelets, they don’t actually make your blood thinner—they just slow down the clotting process to keep strokes, heart attacks, and pulmonary embolisms from happening. Millions take them every day after a clot, surgery, or for conditions like atrial fibrillation. But they’re not harmless. Even small mistakes—like mixing them with certain painkillers or skipping a dose—can lead to serious bleeding or life-threatening clots.
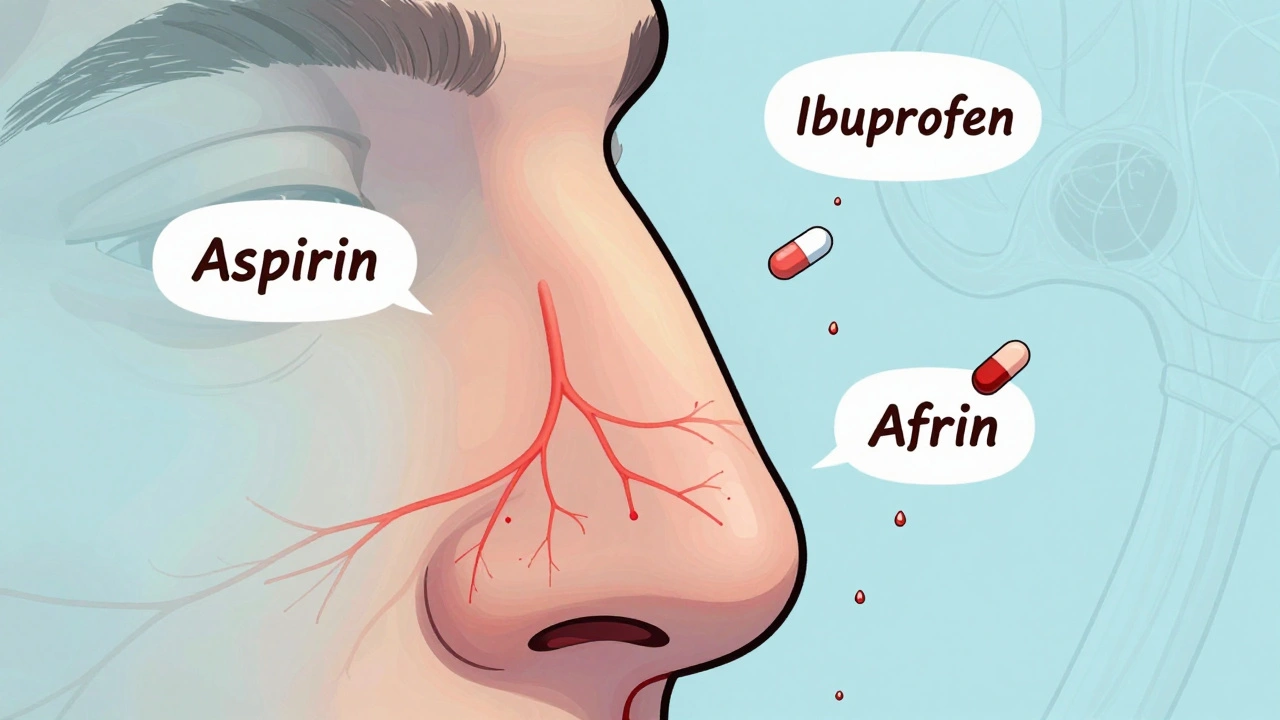
There are two main types: anticoagulants, drugs like warfarin and rivaroxaban that target clotting factors in the blood, and antiplatelets, medications like aspirin and clopidogrel that stop platelets from sticking together. Anticoagulants need regular blood tests to make sure the dose is right, especially warfarin, which reacts with vitamin K in food. Antiplatelets are often taken long-term after stents or heart attacks, but they’re still risky if you’re also using NSAIDs like ibuprofen. That’s why drug interactions, when one medicine changes how another works in your body are such a big deal. A simple cold medicine or herbal supplement can turn a safe dose into a dangerous one.
And then there’s the bleeding risk, the most common and serious side effect of all blood thinners. It’s not just about cuts. A minor bump, a fall, or even a nosebleed that won’t stop can be warning signs. Some people bleed internally without knowing it—headaches, dizziness, dark stools, or unusual bruising could mean something’s wrong. That’s why knowing your meds inside and out matters. You need to tell every doctor, dentist, and pharmacist you’re on a blood thinner. You need to know what to avoid. And you need to understand that taking them isn’t just about popping a pill—it’s about managing a constant balance.
The posts below cover real-world situations you won’t find in pamphlets. From how lithium and NSAIDs can wreck your kidneys when combined with blood thinners, to why older adults are at higher risk for falls and bleeding, to how common OTC meds like diphenhydramine can make things worse. You’ll see how timing, dosage, and hidden interactions can make or break your safety. This isn’t theory. These are the mistakes people make—and the fixes that actually work.